Helicobacter Test INFAI®
Helicobacter Test INFAI is a breath test for the direct, non-invasive detection of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and is now a diagnostic standard and one of the most widely used ¹³C-urea breath tests worldwide. In 1997, INFAI received approval for the Helicobacter Test INFAI (HTI) first time in centralized procedure by EMA in all European countries and it is now available for routine diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection. In mean time HTI is registered in more than 40 countries outside the EU, and is covered by most health insurance companies. The test kit has been optimized for easy use by hospitals and doctors.

Features
Internationally approved
Helicobacter Test INFAI was the first product to be approved by the EMA in 1997 as part of a central procedure in all countries of the European Union. Approval has been extended to 40 countries outside the EU.
Easy test performance
No contraindications
High Sensitivity and Specificity
Approved for children for the first time
Helicobacter Test INFAI has been approved for children aged 3-17 by the EMA for the first time throughout the EU. Until today, it is the only officially approved test for children aged 3-17 years.
Non-invasive
Best reliable test to prove the eradication
Cost-effective
One of the most widely used ¹³C-urea tests worldwide
Helicobacter Test INFAI is a breath test for the direct, non-invasive detection of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. The test is a medicinal product and was the first original product to be approved by the European Commission in 1997 and included in the drug register of all countries in the European Union. As a result, the INFAI test was approved in many countries outside the EU. Helicobacter Test INFAI is one of the most widely used ¹³C-urea breath tests worldwide and today a standard in the non-invasive diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infections. The test has been used in 20 years around 7.0 million times. The test kit has been optimized for easy use by hospitals and doctors. Breath tests can be performed in a suitably equipped hospital laboratory or sent to a qualified laboratory.
Video
Performance of the Helicobacter Test INFAI
The following video shows the performance of the Helicobacter Test INFAI in a clinical study in Nottingham (Titel: Helicobacter eradication to prevent ulcer bleeding in aspirin users: a large simple randomised controlled trial. Sponsor: University of Nottingham, EudraCT Number: 2011-003425-96).
In this study 40,000 subjects in the United Kingdom participated and MS measurement and analysis were performed at the INFAI laboratories in York, England.
Dumbleton J.S., et al. (2015): The Helicobacter Eradication Aspirin Trial (HEAT): A Large Simple Randomised Controlled Trial Using Novel Methodology in Primary Care. EBioMedicine 2: 1200–1204.
Clinical indications for INFAI
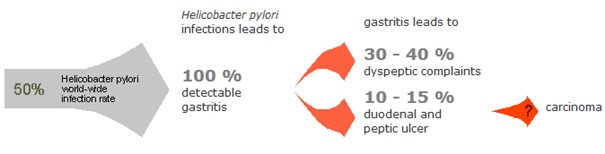
Helicobacter Test INFAI detects a stomach infection by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which is considered the main cause of most types of stomach ulcer, stomach cancer and colon cancer. Stomach cancer is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide and over 80% of gastric cancer cases are attributed to H. pylori infection. The ¹³C-urea breath test is non-invasive and non-radioactive and is recommended by leading gastroenterological associations for use both before and after eradication treatment.
Management of Helicobacter pylori infection The Maastricht V / Florence Consensus Report, Gut 2017
Production of Helicobacter Test INFAI
Quality Assured Production
Equipped with a state-of-the-art automated production line and supervised by experienced and highly qualified staff, INFAI offers a registered ¹³C-urea breath test that is of the highest pharmaceutical quality and reliability. A Quality Manager and QPPV ensure full compliance with our internal operating procedures. Regular quality controls through external audits are carried out by customers, local authorities, federal authorities (BfArM) and EMA.
Production and test performance
The following video gives an overview of the new modern production line in Hagen as well as the performance of the ¹³C-urea breath test and analysis using IRMS and IR spectroscopy method. The kit is serialized for each country according to the european guidlines of falsified medicines.
Quality criteria of Helicobacter Test INFAI
The specificity (98.5%) and sensitivity (97.9%) of Helicobacter Test INFAI are similar or better to traditional invasive diagnostic methods (endoscopy and biopsy). As the breath test indicates the current status of Helicobacter pylori infection, it can be used to confirm successful eradication four weeks after the end of treatment or two weeks after stopping a PPI treatment.
A new breath test with a new test meal (Refex®) for patients taking PPI
50% of all dyspeptic patients are permanently on proton pump inhibitors (PPI). Intake of PPI causes a significant decrease on the sensitivity of non-invasive methods for diagnosis of H.p. infection, such as ¹³C-urea breath test and stool test. Detection of H.p. in patients with dyspepsia therefore required a withdrawal of PPIs for 14 days.
A new formulation of Helicobacter Test INFAI ® now overcomes this inconvenience and offers the following advantages for patients taking PPI:
- Only one-day break of PPI medication necessary
- Simple performance as before
- Safe and reliable diagnosis of H.p. infection
Two clinical trails have been performed for the group of patients taking PPI (see PPI Flyer, publication and EU patent). We applied for Variation Type II by EMA. We hope receiving approval soon.
Comparison of INFAI and Diabact
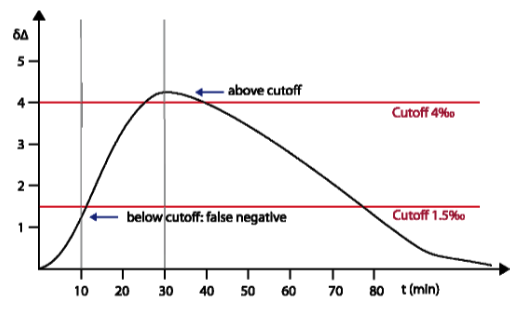
Comparison of INFAI and Diabact Breathtest Diabact uses for the test performance a cut-off point of Δδ= 1.5 ‰ and a sampling time of 10 minutes with a reduced dose (50 mg) of ¹³C-urea for detection of Helicobacter pylori. This test design is not sufficient to get correct results; the short sampling time and lower cut-off point can cause false negative results. This is because maximum urease activity takes between 20 and 30 minutes (also reported by V. Skar et al., Helicobacter 14 (4), 339, 2009). In the beginning, Diabact approved a dose of 2 x 50 mg ¹³C-urea. Later the dose was reduced to 50 mg. This low dose does not reach accuracy sufficient to be recommended in daily practice. In particular it can cause wrong results for patients with a high body weight. Especially after eradication therapy when H. pylori colonization rate is reduced, the overlapping between H. pylori positive and negative results is high, when Diabact test is performed. INFAI validated the cut-off point of Δδ= 4 ‰, a dose of 75 mg ¹³C-urea and a sampling time of 30 minutes by testing more than 9000 patients in several clinical trials inorder to achieve maximum sensibility and specifity. This corresponds with the values most used in the literature (see also scientific discussion at EMA).
Another problem is the application of the ¹³C-urea tablets (by Diabact), which contain citric acid, as the tablet doesn’t dissolve completely within 5 minutes in the stomach fluid. The resulting real residence time in the antrum area and therefore contact to it is too short (10 minutes sampling time) and there’s also no considerable contact to the other stomach areas (fundus). It is known that H. pylori is not equally distributed over all areas in the stomach. Therefore the contact of the ¹³C-urea to all stomach areas is necessary in order to achieve correct results. This is not given by using the Diabact performance. In the INFAI test performance, the patient drinks first citric acid in 200 ml water, then a solution of 75 mg ¹³C-urea in water, so there is no loss of efficiency because all stomach areas are in contact with the dissolved ¹³C-urea.
Formulation of the Helicobacter Test INFAI
The following formulations of Helicobacter Test INFAI are available to the European Union and many other countries:

Helicobacter Test INFAI CLINIPAC 50
Due to increasing demand, INFAI now offers bulk packaging for clinical pharmacies and GPs
- Especially for general practitioners, laboratories and hospitals
- Cost-effective, savings of 20-25% compared to single tests
- Contains test materials for the diagnosis of 50 patients
- Safe and reliable
Quality management and ISO 9001 certification
In May 1999, INFAI GmbH successfully completed the audit for DIN EN ISO 9001 certification for the first time. The quality management system introduced covers all company areas including production, research and development, sales and service. The high quality standards defined within this system ensure the production of safe and high-quality pharmaceutical products. The satisfaction of our customers, and good relations with employees, sales partners and suppliers are the focus of our activities.

More information
For more information about Helicobacter Test INFAI please visit the website of EMA (European Medicines Agency).
Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC) and patient information leaflet (PIL): (Recent versions at EMA in various languages)
Serialization
Implementing the EU’s Falsified Medicines Directive – new line of INFAI packaging
The EU’s Falsified Medicines Directive (2011/62/EU) has been in force since February 9, 2019. The directive is expected to protect the well-being of patients by putting an end to the criminal counterfeiting of medicine.
The Falsified Medicines Directive affects all medicinal products available on prescription.
To implement the directive, the outer packaging of every product shall be furnished with a certificate of authenticity. For the Helicobacter Test INFAI®, this certificate of authenticity is guaranteed by the cellophane wrapping around the single test sampling tubes, and the safety seal on packaging intended for hospital use.
Furthermore, every packet will be furnished with an individual serial number. The serial numbers will be stored in the verification system database of the country in question. Before the product is given out to a patient, usually by a pharmacy, the serial number on the packaging is compared with the serial numbers stored in the database. If the serial number is stored there, the product is authentic, and will be given out to a patient. But if the serial number is not stored there, the product is a counterfeit. The pharmacy will bar these from being given out to patients.
To implement the Falsified Medicines Directive, INFAI has furnished its line of packaging with the latest technology. That way, INFAI can apply all the required safety features, including individual serial numbers, in high quality, and to transmit all the necessary data to the databases of the national verification systems. Thanks to these measures, we can guarantee patients the highest possible level of protection against counterfeits of our products.
References
- World Health Organization WHO (1994)
Classification of Helicobacter pylori as a category 1 carcinogen. (Lancet 344) - Current European concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection
The Maastricht Consensus Report. (Gut 1997; 41: 8-13) - Current concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection
The Maastricht 2-2000 Consensus Report. (Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2002; 16: 167-180) - Current concepts in the management of Helicobacter pylori infection
The Maastricht III Consensus Report (Gut 2007; 56: 772-781) - Management of Helicobacter pylori infection
The Maastricht IV / Florence Consensus Report (Gut 2012; 61: 646-664) - Management of Helicobacter pylori infection
The Maastricht V / Florence Consensus Report (Gut 2017; 66: 6-30)
INFAI publications
- Dumbleton J.S., et al. (2015)
The Helicobacter Eradication Aspirin Trial (HEAT): A Large Simple Randomised Controlled Trial Using Novel Methodology in Primary Care. EBioMedicine 2: 1200–1204 - Tepeš B., Malfertheiner P., Labenz J., Aygen S. (2017)
Modified Helicobacter test using a new test meal and a ¹³C-urea breath test in Helicobacter pylori positive and negative dyspepsia patients on proton pump inhibitors. World J Gastroenterol 23(32): 5954-5961. - Significant decrease in prevalence of H. pylori in the Czech Republic.
Bureš et al.; WJG, 2012, 18(32): 4412. - Comparison of non-invasive tests to detect Helicobacter pylori infection in children and adolescents
Results of a multicenter European study.
Mégraud, F. et al.; The Journal of Pediatrics, 2005, 146(2): 198. - Albarti, A. (2002)
Utility and acceptability of INFAI C-13-urea breath test. BMS 324: 485 - (2001)
INFAI breath test in general practice. Cleveland Med. J. 4: 116-8. - Labenz J., Aygen S., Hennemann 0., Peitz U., Tillenburg B., Börsch G., Stolte M. (1995) Validity of a novel biopsy urease test (HUT) and a simplified ¹³C-urea breath test for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection and estimation of the severity of gastritis. Digestion 57(6): 391-7.
- Labenz J., Stolte M., Aygen S., Hennemann O., Bertrams O., Börsch G. (1993)
Qualitative und semiquantitative invasive und nicht-invasive Diagnostik der Helicobacter pylori-Kolonisation der gastralen Mukosa. Z Gastroenterol 31(7-8): 437-43.
Studien zum Helicobacter Test INFAI
Studie: PPI; Eudra CT Number: 2008-008010-39
The Sensitivity and Specificity in Helicobacter Pylori Positive and Negative Patients with Dyspepsia Taking Proton Pump Inhibitors. Sponsor: INFAI
Studie: Aptalis; Eudra CT Number: 2010-019064-36
Efficacy and Safety of PYLERA (Bismuth Subcitrate Potassium, Metronidazole, and Tetracycline Hydrochloride) With Omeprazole Given x 10 Days in Subjects Who Failed Treatment for Eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Sponsor: Aptalis
Studie: HEAT; Eudra CT Number: 2011-003425-96
Helicobacter eradiation to prevent ulcer bleeding in aspirin users: a large simple randomised controlled trial (HEAT). Sponsor: University of Nottingham
Dumbleton J.S., et al. (2015): The Helicobacter Eradication Aspirin Trial (HEAT):
A Large Simple Randomised Controlled Trial Using Novel Methodology in Primary Care. EBioMedicine 2: 1200–1204
Studie: PPI; Eudra CT Number: 2017-001369-25
The Sensitivity and Specificity of the Modified Helicobacter Test INFAI Using New Test Meal with ¹³C-Urea Breath Test in Helicobacter pylori Positive and Negative Patients with Dyspepsia and GERD Taking Proton Pump Inhibitors.
Sponsor: INFAI
Patente
PPI-Patent
EP1685851, Method for the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection and a diagnostic kit for performing the method,
European Patent, 13.05.2009
US20030032081, Method for the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection and a diagnostic kit for performing the method,
US Patent, 13.02.2013
Heliblue Patent
EP1415159, Method and Diagnostic Kit for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori,
European Patent, 24.10.2007
US7033838, Method for the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection and a diagnostic kit for performing the method,
US Patent, 25.04.2006
WO2003014744, Method and Diagnostic Kit for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori,
International Patent, 22.02.2003
